How to Connect Product Work to Revenue

Businesses only have a limited amount of money to allocate and spend while developing their products.
If you, as a project manager, don’t link your work to making money, you might be working on things that don’t help the organization as a whole. What’s the point if you don’t help your company get returns on its investment?
If a product team doesn’t know how much money they’re making, their work doesn’t fit with the business plan.
There is a chance that the work of the product team may be counterproductive for the business. You can’t know, though, unless you connect it to revenue.
Establishing relationships to revenue is of greater significance for B2B product teams than for B2C teams because they are closer to the stage of a deal. A lot of direct-to-consumer companies make money through ads and subscriptions.
When it comes to B2C, product managers don’t have to worry about how customers pay for the product. This lets them focus on what the product is really worth.
B2B goods make it very likely that product teams will be pulled into deals, whether you work with small to medium-sized businesses or bigger companies.
Products help bring about wins and stop losses. At the very least, that means that income is a larger component of daily life in B2B product management.
Let’s understand the connection between Product and Revenue and how you can define their relationship in your workplace.
What is the Connection Between Product Work and Revenue?
The connection between product work and revenue is vital for any business. Essentially, product management plays a crucial role in driving revenue by ensuring that products meet market demands and customer needs.
This begins with understanding the target audience and identifying problems that the product can solve effectively.
A key concept here is product-market fit, which means creating a product that customers want to buy. When a product fits well in the market, it drives sales, leading to increased revenue.
But is the idea of a product fitting itself enough to achieve product revenue? No.
Hence, it’s the role of a product manager to focus on optimizing the product lifecycle, from development to launch and beyond, ensuring continuous improvement based on customer feedback.
Revenue generation is not just about initial sales; it’s about building long-term relationships with customers.
Product managers work closely with sales, marketing, and customer support teams to enhance the overall customer experience, encouraging repeat purchases and loyalty.
Moreover, you should be constantly using data-driven strategies to make informed decisions, aligning product features and enhancements with business goals. By prioritizing features that deliver the most value to customers, you can maximize the product’s profitability.
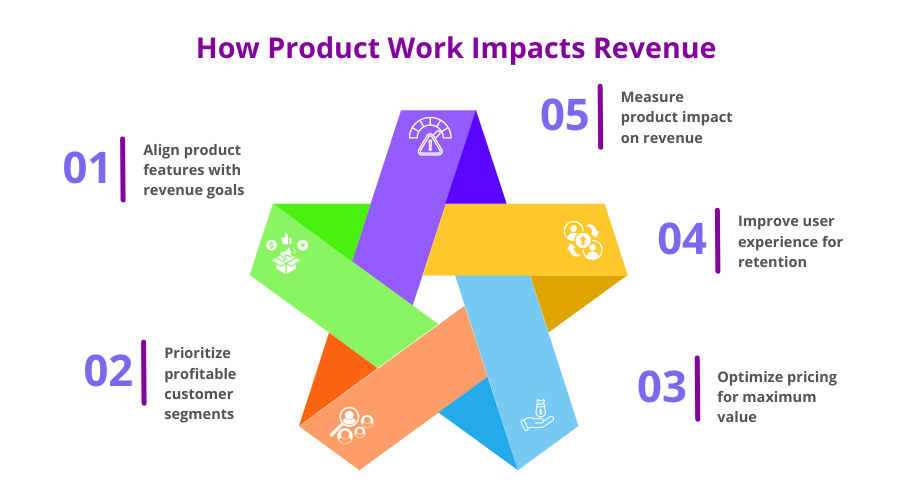
In short, efficiently connecting product work and revenue makes sure that the product not only reaches the market but also thrives.
What are the Key Metrics and KPIs
KPIs play a pivotal role in understanding the connection between product work and revenue.
These indicators will help you how well a product is performing in the market and how it impacts the company’s bottom line. Here are some of the most important ones:
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC):
This metric measures the cost of acquiring a new customer. A lower CAC indicates that your product is effectively attracting customers without excessive spending, which directly influences profitability.
Formula: Total Cost of Sales & Marketing / No. of customers acquired
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV):
CLTV estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer over time. A higher CLTV means that customers are not only purchasing but also sticking around, contributing to sustained revenue.
Formula: Customer Value * Average Customer Lifespan
Churn Rate:
This KPI tracks the percentage of customers who stop using your product over a specific period. A low churn rate suggests strong customer retention, which is essential for long-term revenue growth.
Formula: Lost Customers / Total Customers at the Start Period
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR):
For subscription-based products, MRR tracks the predictable revenue generated each month, providing insight into the product’s financial stability.
Formula: Number of subscribers under a monthly plan * ARPU
Conversion Rate:
This metric measures the percentage of users who take a desired action, such as making a purchase. High conversion rates indicate that your product is effectively turning prospects into paying customers.
Formula: (No of Conversions / Total Visitors) * 100
Average Revenue Per User (ARPU):
ARPU measures the average revenue generated from each user, helping to gauge the product’s overall financial performance.
Formula: Number of subscribers under a monthly plan * ARPU
What are the Strategies for Connecting Product Work to Revenue
Connecting product work to revenue requires strategic alignment between product development and business goals. How can you achieve this? Here are some effective strategies:
Aligning Product Goals with Business Objectives:
Start by ensuring that your product goals are in sync with the company’s broader business objectives. This alignment will make sure that every product decision is driving toward key revenue targets, whether it’s market expansion, customer retention, or upselling.
Creating a Revenue-Focused Product Roadmap:
Develop a product roadmap that prioritizes initiatives with the highest revenue potential. This makes sure that you focus on features and enhancements that directly contribute to financial growth.
You can ensure that your product development efforts are strategically geared toward maximizing revenue.
Focus on Product-Market Fit:
Invest time in understanding your market and customers. A strong product-market fit leads to higher adoption rates, driving revenue growth as your product effectively meets customer needs.
Align with Sales and Marketing:
How do you make sure that your product is positioned in the market effectively? Collaboration. SIt with your Sales and Marketing to understand the nuances.
Close collaboration with sales and marketing will help you attract the right customers and boost revenue.
Implement Pricing Strategies:
Experiment with pricing models to find the optimal balance between customer value and revenue generation, whether through tiered pricing, freemium models, or value-based pricing.
Measure and Iterate:
Regularly monitor KPIs such as Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), Churn Rate, and Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR). Use these insights to refine your strategy, ensuring that your product work consistently drives revenue growth.
You need to strategically aligning product goals with business objectives and creating a revenue-focused roadmap.
In this way, you can ensure that your product efforts not only meet customer needs but also significantly contribute to the company’s financial success.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
1. Netflix: Data-Driven Product Decisions
Netflix, the global streaming giant, has consistently leveraged data analytics to guide its product strategy.
They use vast amounts of data to understand viewer preferences, predict trends, and personalize the user experience. This data-driven approach allows Netflix to recommend content that keeps users engaged, reduces churn, and attracts new subscribers.
Revenue Impact:
By utilizing data to make informed decisions, Netflix has been able to maintain high engagement levels and increase subscriber growth.
This focus on personalization and user satisfaction has translated into impressive financial results. As of 2023, Netflix’s revenue exceeded $30 billion, with over 230 million subscribers worldwide.
Harnessing the power of data analytics to drive product decisions can significantly enhance customer engagement and revenue.
By understanding customer behavior and preferences, companies can tailor their products to meet user needs, resulting in higher retention and more robust financial performance.
2. Slack: Building a Product That Sells Itself
Slack, the popular team communication tool, is a prime example of how a product with a clear focus on user experience can drive substantial revenue.
Slack’s strategy centered on creating a product that users loved from the start, leading to rapid organic growth.
By focusing on ease of use, seamless integration with other tools, and continuous improvement based on user feedback, Slack was able to quickly build a loyal customer base.
Revenue Impact:
Slack’s focus on delivering an exceptional user experience resulted in high user adoption rates and low churn.
The product’s viral nature—where satisfied users invited colleagues—allowed Slack to grow rapidly without heavy reliance on traditional sales or marketing. By 2019, Slack had more than 10 million daily active users and was generating over $630 million in annual revenue.
Investing in a user-friendly product that solves real problems can lead to organic growth and significant revenue.
Ensuring that the product experience is intuitive and valuable encourages word-of-mouth marketing, reducing customer acquisition costs and driving sustainable revenue.
How to Use Technology and Tools
Leveraging technology and tools is essential for connecting product work to revenue. It allows you to track, analyze, and optimize their strategies effectively.
Here’s how you can utilize technology and tools to ensure that your product efforts are driving revenue growth:
Tools for Tracking and Analyzing Product Impact on Revenue
To understand how your product influences revenue, it’s crucial to use the right tools for tracking and analysis. These tools help in collecting data, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), and gaining insights into customer behavior.
Product Analytics Platforms:
Tools like Mixpanel, Amplitude, and Heap provide deep insights into user interactions with your product. They help you track user engagement, conversion rates, and feature adoption, offering a clear view of how these factors contribute to revenue.
If you understand which features are most used and which lead to conversions, you can make informed decisions about where to focus your development efforts.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems:
Integrating your product data with CRM systems like Salesforce or HubSpot can provide a comprehensive view of customer behavior across different touchpoints.
This integration allows you to track the customer journey from initial contact to purchase and beyond, linking product interactions directly to sales outcomes.
Revenue Analytics Tools:
Tools like ProfitWell and Baremetrics specialize in revenue analytics, particularly for subscription-based products.
They offer insights into metrics like Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), and churn rate.
If you analyze these metrics, you can identify trends and opportunities to optimize your product for better revenue performance.
Product Management tools
A great product management tool can efficiently connect product work to revenue by streamlining workflows, aligning teams, and ensuring that product decisions are data-driven and customer-focused. Tools like Chisel, an all-in-one AI-powered PM tool, excel in this area by integrating roadmaps, team alignment, and user feedback into one platform.
This comprehensive approach helps you prioritize features that drive revenue, ensure team efforts are aligned with business goals, and incorporate user feedback to continually optimize your product for better financial performance.
Using Data Analytics to Drive Product Decisions
Data analytics is the backbone of revenue-focused product management. It enables product teams to make informed decisions that align with business objectives and customer needs.
A/B Testing:
A/B testing tools like Optimizely and Google Optimize allow you to experiment with different versions of your product features, designs, or pricing models.
By comparing the performance of these variations, you can determine which option generates the most revenue, leading to data-driven decisions that enhance product effectiveness.
Cohort Analysis:
Tools like Mixpanel and Google Analytics enable cohort analysis, which helps you track how different groups of users behave over time.
By understanding the retention and revenue patterns of these cohorts, you can tailor your product strategy to target the most profitable customer segments.
Predictive Analytics:
Leveraging predictive analytics through tools like Pendo or Gainsight can help you anticipate customer behavior and potential revenue outcomes.
These tools analyze historical data to predict future trends, allowing you to proactively adjust your product strategy to maximize revenue.
Customer Feedback and Sentiment Analysis:
Tools like Qualtrics and Medallia provide insights into customer satisfaction and sentiment.
By analyzing this feedback, you can identify areas where your product may be falling short and make improvements that increase customer loyalty and revenue.
How to Overcome Challenges
From aligning diverse teams to managing conflicting priorities, there are several hurdles that can impede the link between product work and revenue. Here’s an exploration of these common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
Common Challenges in Connecting Product Work to Revenue
Misalignment Between Product and Business Objectives:
One of the most prevalent challenges is the misalignment between product goals and overall business objectives.
While product teams may focus on user experience, innovation, or feature development, the broader business might prioritize revenue growth, market share, or cost reduction.
This disconnect can result in product decisions that don’t contribute effectively to revenue generation.
Lack of Clear Metrics and KPIs:
Without clear metrics and KPIs, it’s difficult to measure how product work impacts revenue.
Product teams often struggle to identify the right indicators that link product success to financial performance, leading to efforts that may improve the product but not necessarily the bottom line.
Data Silos and Limited Access to Information:
In many organizations, data is spread across various departments and tools, creating silos that hinder the ability to track and analyze the product’s impact on revenue.
Limited access to comprehensive data makes it challenging for product managers to gain a full picture of how their work drives financial outcomes.
Balancing Short-Term Revenue Goals with Long-Term Product Vision:
Another challenge is balancing the pressure to meet short-term revenue targets with the need to invest in long-term product development.
This can lead to a focus on quick wins at the expense of strategic initiatives that would provide greater revenue potential in the future.
Resistance to Change:
Implementing a revenue-focused approach often requires cultural shifts within the organization.
Teams may resist changes to processes or priorities, particularly if they’ve been accustomed to focusing on metrics like user engagement or product innovation rather than revenue.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
Align Product Goals with Business Objectives:
To overcome misalignment, establish clear communication channels between product teams and executive leadership.
Regularly review and update product goals to ensure they are in sync with the company’s financial objectives. Involve product managers in strategic planning sessions, so they have a clear understanding of the business’s revenue goals and can align their efforts accordingly.
Break Down Data Silos:
Encourage cross-departmental collaboration and invest in integrated tools that provide a unified view of customer data, product usage, and financial metrics.
Tools like Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) can consolidate data from various sources, giving product managers the comprehensive insights needed to link product work to revenue.
Balance Short-Term and Long-Term Goals:
Develop a product roadmap that balances short-term revenue-generating initiatives with long-term strategic projects.
Communicate the importance of both to stakeholders, emphasizing how long-term investments in product development can lead to greater revenue potential over time.
Use scenario planning to anticipate the trade-offs and ensure that both immediate and future revenue goals are considered.
Foster a Revenue-Focused Culture:
To overcome resistance to change, foster a culture that values revenue impact as much as user engagement or product innovation.
Provide training and resources to help teams understand the connection between their work and the company’s financial health.
Highlight success stories where product initiatives have directly contributed to revenue, reinforcing the importance of this focus.
Leverage Agile Methodologies:
Use agile methodologies to remain flexible and responsive to changes in the market or business objectives.
Agile practices, such as regular sprint reviews and retrospectives, can help product teams stay aligned with revenue goals and quickly adapt to shifting priorities.
Conclusion
In the complex landscape of product management, connecting product work to revenue is critical for a company’s growth and sustainability. How do you define success here?
The key to success lies in aligning product goals with business objectives, leveraging data-driven insights, and focusing on metrics that directly influence the bottom line. As covered earlier, they include stuff like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV).
Adopting strategies like creating a revenue-focused product roadmap and fostering collaboration across departments is crucial. Here, you can ensure that efforts are not only customer-centric but also financially impactful.
To effectively link product work to revenue, it’s essential to foster a culture that prioritizes financial outcomes alongside innovation and user experience.
Regularly revisit your product strategy to ensure it aligns with evolving business goals, and use technology and tools to track progress and make informed decisions.
To conclude, you and your product team are now ready to drive both customer satisfaction and sustained revenue growth now effectively than ever.
