Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control

The distinction between quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) can easily create confusion (QC).
Although there is a clear difference between the two, some people use the names interchangeably.
Your company can develop the best products imaginable and comply with the appropriate standards using QC and QA.
Understanding both words is, therefore, crucial.
What Is Quality Assurance?
Let’s begin with separating the two. What is quality, and what is assurance?
Quality refers to the state of being fit to use.
It means fulfilling the requirements and expectations of the consumer in terms of the product’s usefulness, appearance, dependability, durability, and value.
Assurance is a confident statement made about the goods. It guarantees a good outcome for a good or service.
Combining both of these elements will give you quality assurance.
A strategy to guarantee the quality of software goods or services offered to clients by a business is known as quality assurance.
Quality assurance aims to increase the software development process’s efficiency and reliability by the established quality standards.
Testing for quality assurance is known as QA.
What Is Quality Control?
Quality control (QC) ensures that a specified range makes a product of quality criteria or that it satisfies the consumer’s needs.
Establishing a culture of excellence among management and staff is necessary for quality control.
You accomplish this through staff training, the development of product quality benchmarks, and product testing to look for statistically significant variances.
Splitting the production tasks between employees helps ensure that everyone is carrying out tasks for which they are adequately trained. This limits the margin for error and lowers the likelihood of workers feeling overwhelmed with their duties.
The various approaches to quality control are the taguchi method, six sigma, an x-bar chart, and 100% inspection mode.
How To Perform Quality Assurance
Whether you’re making cookies or computers, your product should provide consistent high quality to your customers.
The term “quality assurance” describes all the processes and procedures involved in ensuring a product or a service complies with customer expectations consistently.
Customer Input
If you want to set up a business baking cookies, you expect your customers to love them and share them with their friends about them.
You might start by asking family and friends what qualities they look for in cookies as a first step.
Based on their suggestions, you might declare to satisfy your customers’ needs. The cookie must have a soft base, be 2 inches in diameter, and probably include raisins.
This phase is essential for formulating your recipe and establishing your product’s quality standards. The recipe outlines the steps to follow to make your cookie.
Want to receive feedback and recommendations from your customers? Then you need to check out Chisel. Chisel is a customer-oriented product management software that helps you to take your business to next level, giving you a competitive edge.
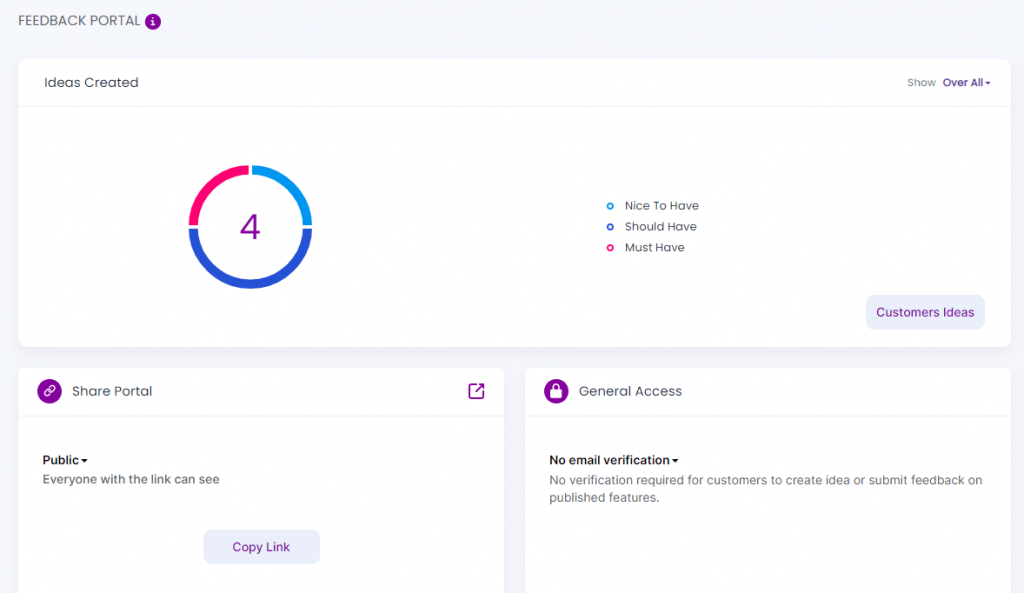
With the help of Chisel’s Feedback Portal, collecting and managing customer feedback and recommendations feels like a walk in the park.
Product Features
The consumer suggestions gave the requirements for cookies, considering factors like cookie size and texture.
You must handle every production element to ensure that every cookie meets these requirements beginning with the contents.
To control manufacturing, create a set of guidelines or practices. These could involve techniques for examining cookie manufacture and creation.
For instance, if the diameter of the cookie is essential to its quality, measure each cookie to ensure that it is 3 inches in diameter.
Control and Validation
As your company expands and you produce more cookies, you become aware of how expensive and timely it is to complete a 100% assessment.
Making sure that a substantial proportion of your cookies have a diameter within the acceptable range would be a wiser use of your ingredients.
You often accomplish this by creating a method that can tightly regulate the diameter of the cookie.
Process validation is the name given to this process improvement. Check that all equipment is set up and operating as intended by the manufacturer as part of the process validation.
When you utilize different batches of raw materials or alter the configuration of the equipment within a narrow range, you should also confirm that the technique, the equipment, and the operator create a 3-inch cookie.
Non-conformity
After a thorough inspection, nonconforming items gets manufactured, inspected, and then discarded.
Using methods to reduce nonconformity, the upgraded process with process validation has significantly reduced the percentage of nonconforming parts.
How To Perform Quality Control
When you think of quality control, you picture manufacturing companies checking items for defects.
Quality control procedures apply to all business models, whether B2B or B2C, product- or service-based.
Quality Standards
You might need to conform to quality standards imposed by an outside party in some businesses, such as a trade association, municipal health and safety officer, or a government regulator authority.
Others lack established standards of quality, so you’ll have to develop your own.
Various quality control standards will apply to different parts of your company. But, they should all be measured objectively.
For instance, “sounding friendly on the phone” is not a meaningful requirement if you’re creating quality control guidelines for your customer support staff.
Focused Decisions
Naturally, you want to ensure that your business is of the highest caliber.
Therefore, start by concentrating on essential metrics, those that have the greatest impact on your revenue and customer satisfaction.
This can help you and your team avoid overburdening while enabling you to get outcomes swiftly.
For instance, maintaining clean restrooms is something to check in your quality control program if you run a restaurant—but it’s not the most crucial.
Fast and precise order delivery to clients is a more crucial criterion because it directly impacts their pleasure and the quality of their experience in all types of restaurant management.
Review Your Results
Many business software, including customer relationship management (CRM), accounting programs, and customer support and finance tools, allow you to personalize the data you gather and use dashboards to view it quickly.
To determine how successfully your business follows its quality standards, frequently analyze your statistics.
Feedback
To create a complete picture of the quality of a product or service, use quantitative feedback from outside sources, such as survey responses, internet ratings, reviews, and net promoter scores (NPS).
Obtain regular input from your staff as well. How effectively are the operating procedures delivering quality? How might they be made better? And much more.
Improvements
Don’t stop once you’ve reached your quality control goals.
If you run a domestic cleaning service, you can increase your business by 25% simply by reducing the time it takes your maids to complete a clean by 25%. It is a huge saving in terms of time and resources, and it’s well worth doing if you want to increase your business.
Quality control proves that there is always scope for development and that even tiny adjustments can greatly impact.
Examples of Quality Assurance
Security
Usually, quality control makes sure that items like surveillance gear or cybersecurity software are error-free and match their standards.
The security threats will increase if the security equipment has a flaw.
Quality control issues resolve potential concerns, even if cybersecurity is more of an IT team’s responsibility.
Quality Assurance gives protective computer training to combat these circumstances.
Everyone can operate the same system smoothly if they receive training. Performance testing and code reviews could be a part of this training. Don’t forget about the importance of SOC 2 audits. With these audits, you can make sure you have adequate security policies and controls in place to safeguard your customer’s data.
Food Safety
Most businesses use customer service departments to communicate customer complaints.
It is the responsibility of the quality assurance teams to deliver safe food for consumers continually.
For instance, to guarantee customer safety, quality assurance must examine if the labeling of a food product covers all of its contents and allergy cautions.
If difficulties arise, the quality assurance teams must identify what went wrong, correct it, and ensure it doesn’t happen again.
Food recalls may be undertaken if a safety concern is discovered in the product to address the problem and enforce safety standards.
Design
The functioning of a product must be taken into account by quality assurance teams to offer customers comfort and happiness.
A product needs to be both practical and visually beautiful to satisfy buyers.
For instance, quality control might need to consider client grievances about product safety issues.
Following the installation of the fixes, quality control notifies customers of a product recall and asks them to either pursue the necessary repairs or demand a substitute.
Examples of Quality Control
Fast Moving Consumer Goods
Every bottle in an apple juice factory goes through a basic test, and several units from each batch get sent for a detailed examination.
Full testing uses pseudorandom numbers for selecting the units.
Vehicles
Every component produced by a train producer gets subjected to a rigorous inspection that includes manual and automated verifications.
Food Services
An airline evaluates the quality of its meals with statistically significant samples that authenticate several food safety measures.
A different quality control program collects samples less frequently for sensory analysis to ensure the meals taste well.
Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Understanding the gap between quality assurance and quality control is vital to maintaining quality standards in the QA and QC processes.
Although they are interchangeable, they are two distinct processes at various times. They differ in:
Focus
With an emphasis on the production process, QA seeks to prevent errors. This quality process is proactive.
Quality control aims to find and fix errors in the final product. Hence, quality control is a reactive process.
QC concerns would also prompt a QA evaluation.
When test findings are irregular, CAPA should take place to investigate the problem’s fundamental cause and improve procedures to ensure it doesn’t happen again.
Goal
QA aims to improve testing and development procedures so that errors do not appear throughout the product’s development.
Whereas, before a product is released, QC is used to find any flaws once you have developed it.
Responsibility
Quality assurance is the responsibility of everyone in the product development team.
Training, documentation, and review within the workforce are part of quality assurance (QA) operations, even though the quality department and management group are often in charge of the quality management system (QMS).
But in quality control, a specific team is typically in charge of quality control, which involves checking the product for flaws.
The quality control team adheres to SOPs and records findings using standardized tests for validating processes and testing products.
Statistical Techniques
Both QA and QC can benefit from using statistical tools and techniques.
They are known as Statistical Process Control (SPC) when applied to operations (process inputs & operational parameters) and become a quality assurance component.
Statistical Quality Control (SQC) is the term used to describe the application of statistical tools and methodologies to finished goods (process outputs) and is a subset of quality control (QC).
Conclusion
Understandably, words like “quality” hold weight when fast delight, short attention spans, and ever-improving technology are at our hands.
Businesses’ brand image and the confidence they inspire may never be more vital as they adjust to satisfy these contemporary demands and today’s always-connected consumer.
That’s it for today. If you’re new to product management and are looking for quality service, try Chisel’s free forever today!
