Agile Product Management: What, Why & How to Nail It

Agile product management is a new form of product management in the market and is gaining rapid popularity.
Agile, meaning quick to adapt, according to the market situation.
A product manager with Agile skills can manage products better by following Agile practices.
Agile product management has emerged as a new model for managing software products.
Agile is used for this type of approach because Agile methodologies mainly focus on software projects’ needs.
The agile product management approach has its roots in agile methodologies. Agile mythologies’ objective is to make the best use of agile concepts in the context of a product (rather than a project).
Agile product management is a relatively new approach to developing and managing software products. However, organizations have used agile development in software development for more than a decade.
Agile techniques focus on the needs of projects instead of following a predefined plan.
The agile movement also values working software over comprehensive documentation and customer collaboration over contract negotiation. Furthermore, responding to change instead of following a plan.
Agile product management is agile in this context: The technique implementation applies to new product management, not just software projects.
For instance, product development allows small cross-functional teams to define their product process and identify what features they should include in a product. Additionally, give each member autonomy to lead their part of the work.
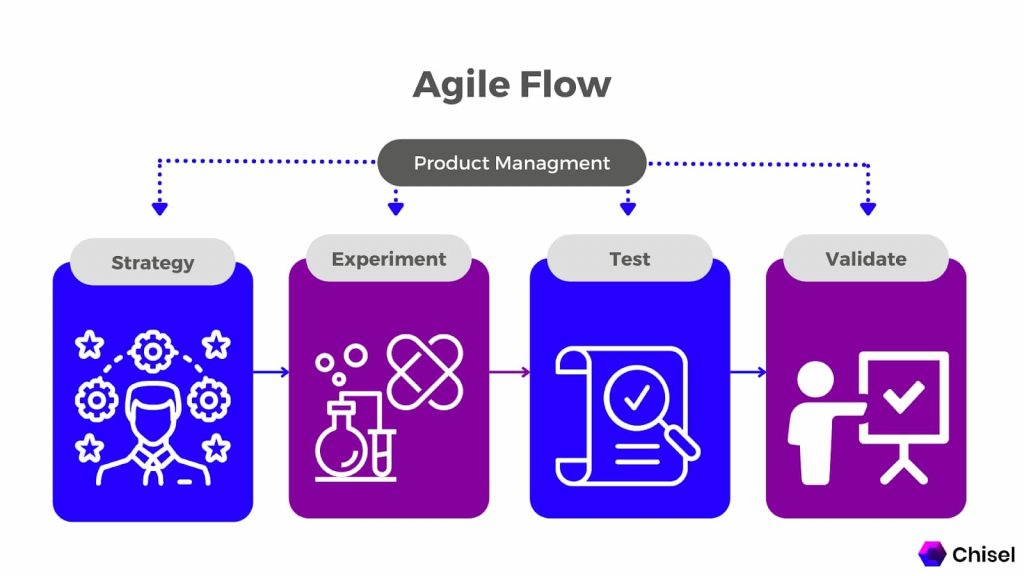
What Is Agile Product Management?
Agile Product Management Definition
Product management is driving a product through several iterations in agile software development. Agile product management is a highly adaptable approach to conventional methods since agile initiatives are more flexible.
Agile product management is an iterative process of managing new products. It aims to release high-quality products quickly and respond to a rapidly changing marketplace.
The rules, values, principles, expectations, and product management tools are all new in agile product management. In agile product management, the priority is to maximize the value realized by a customer.
In agile development, one does not rely on detailed requirements from customers upfront. Instead, agile methodologies prioritize working software over comprehensive documentation and customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
For example, Kanban boards are an agile tool that facilitates team collaboration and transparency by determining priority on the roadmap.
There is no need for extensive upfront planning and documentation in agile product management, as it can produce better products much faster. The agile motto: “If it doesn’t work, do and say what does,” shows that agile has a culture of trying new things and not running in place.
What is the Best Agile Product Management Software?
The best Agile Product Management software is one that seamlessly combines flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity to help product teams adapt to changing market demands and deliver high-quality products efficiently. It should offer robust tools for roadmapping, team alignment, and customer engagement, enabling teams to prioritize effectively, iterate quickly, and stay connected to user needs.
Among the top solutions in this space is Chisel. Chisel stands out as a holistic Agile Product Management platform, integrating the three critical pillars of product management: roadmapping, team alignment, and customer feedback. Its emphasis on collaboration tools ensures teams can work together seamlessly, while its one-stop-shop approach simplifies workflows and empowers product managers to focus on delivering exceptional value. For teams looking to elevate their Agile practices, Chisel is the ultimate solution.
Pros and Cons of Agile Product Management
Agile methodologies are enough to observe market conditions and customer needs keenly. But, everything has its benefits and drawbacks, and so does agile product management. However, pros and cons vary according to the situations and goals of agile product management.
Here are the pros and cons:
Pros:
- Agile offers more flexibility. Agile development does not mean planning. It is more pliable than the Waterfall method and gives more room to alter product development and management processes.
- Agile gives a competitive advantage. Agile products are more likely to produce flexible, innovative, and user-friendly products. Agile has become crucial for developing business in the fast-moving global economy. Flexibility and market acumen helps to perform better in the market.
- Agile is faster than traditional product management. Agile product managers usually spend less time preparing plans and writing documents. They take more time on customer interaction, market observance, and the making of new strategies. This feature immensely helps to bring the product to market much faster.
- Agile facilitates change. Agile teams can respond faster to changes in the business environment by modifying plans, priorities, and deadlines for agile products.
- Agile roadmap explains the ‘why.’ Agile planning focuses on product requirements. It does not focus on product management. Also, it does not involve defining the reason for product development, the purpose, and who it will serve.
- Agile facilitates agile failures. Agile teams capture and document learnings from the agile process (to avoid repeating mistakes.) Rather than relying on lengthy reports to reach the same goal.
- Agile promotes transparency. Agile product managers are more visible in agile products. This expectation is because continuous integration forms the backbone of agile. People have to be more visible, promoting transparency to do that efficiently.
- Agile requires agile skills. Agile products require different personalities, skills, and abilities than traditional Waterfall approaches.
- The Agile roadmap offers more alignment. Agile product management provides a more aligned roadmap than the traditional Waterfall method.
- Agile encourages continuous discussion. Agile product management is necessary to keep track of continual debate. Discussion entails each product strategy, vision, mission, and agile objectives.
- Another agile benefit is its setup for scalability. The organization can add or remove team members with little disruption to the production schedule.
- Agile is not limited to development teams. Any organization that takes a more flexible approach can use agile.
- Agile requires a paradigm shift for many product managers and stakeholders. The agile team may not know how to do everything right away. But they can quickly determine what works best in a given situation and respond accordingly.
- The agile framework allows for minimizing waste.
- Agile offers better customer satisfaction and a higher return on investment.
- Agile provides more opportunities to develop a product as per the requirement of customers and market conditions.
- Agile allows adapting to fast changes which might occur along the way.
- Agile consumes less time than conventional methods of developing a product. Agile provides more chances to recover.
- Agile allows easy and fast access to customers closer to the developers.
Cons:
While Agile provides many advantages, it also has some cons that need to be considered seriously before using agile product development:
- The Agile roadmap can get outdated quickly since it is an ongoing process. This roadmap needs to be updated constantly.
- Agile is not suitable for highly structured and planned products. Agile focuses on the iterative development process rather than highly structured products. Agile can turn into chaos when applied to highly organized processes.
- Having separate teams in Agile doesn’t work well with Agile. Agile is not suitable for different groups to work on a product. Teams have to interact with each other constantly. They should be in constant communication to do so correctly, which isn’t possible with separate teams.
- Agile can make teams too focused on the products. Rather than business needs, resulting in agile failures sometimes.
- Pushing changes constantly throughout the agile process disrupts the agile flow and makes it difficult to track progress. This agile model may be suitable for some products. But agile is not good for PMOs as it can sometimes become chaotic.
- You can apply the agile philosophy to any organization. This claim is misleading as the agile methodology may not work in some organizations. Remember that agile may not work for highly structured and planned products.
Agile product management vs. Project management
Product management is an internal company operation that handles the planning, scheduling, production, and promotion of a product. It is applicable throughout all phases of its life cycle.
Project management, in contrast, is the procedure of using processes, techniques, expertise, and skills. It also includes the knowledge to meet a project’s objectives.
Competent product managers accept full responsibility for a product’s total and long-term performance. Several skills, such as managing time and problem-solving, are necessary for product managers to succeed in this role.
A product manager’s job is to implement product performance and market research, emphasizing the “what” rather than the “how.” They also use appropriate product management tools for efficient work output.
Their task is to look at the big picture and determine the product’s long-term direction. They mainly depend on the evolution of the client’s demands.
On the other hand, project managers are in charge of completing a project on time and under budget, with a defined start and end. Also, preferably following a product roadmap. There is various product roadmap software that comes in handy here.
Project managers supervise and manage the product’s development. It is done by coordinating accessible resources and addressing challenges and hazards until completion.
Maintaining the project scope is among the most challenging duties for a project manager because they must manage time, budget, and quality.
Project managers should increase prices or reduce scope if a project’s deadline gets delayed to maintain quality.
What Are Agile Product Management Best Practices?
Agile product management helps motivate teams to work more efficiently. However, as the development phase comes to a close, teams may wonder if the solution they came up with turned out great or not.
How can you move swiftly in today’s highly competitive marketplaces? While still offering maximum value to the company and its customers?
The answer is to move quickly and strategically. Establishing goals and creating and presenting a precise product roadmap are two ways product managers do this. Here are some guidelines for agile product teams to follow:
Begin with a plan
Centering your effort on a tangible goal. The agenda encompassing your product’s objectives and strategy is the best means of moving quickly. While still providing value.
The vision of your product or what you want it to accomplish in the future is its fundamental essence. Your objectives are more time-bound, defining what you aim to do in the coming quarter or year to help you realize your vision. Goals may help you and your team stay on track by giving you and your team a real direction so you can make adaptive decisions.
Gather customer recommendations
Your vision, goals, and clients should influence your roadmap. You can use customer surveys or internal channels like support or sales to discover fresh ideas. However, be mindful of iterating on every point of feedback you receive.
Users will be able to define the problem they are having, but they may not be able to explain the solution. Implement an internal scoring program that utilizes objective criteria to score prospective strategies. These strategies guarantee that you only execute the most beneficial ideas.
Establish the scope of the significant task
For the work that will assist you in attaining your objectives, you may also need broad divisions. Your efforts, epics, and themes define your work here. “Boost the mobile experience” or “work on improving performance” are two instances.
For more strategic work, you can place individual elements and user stories in these categories.
You can ensure that everything you do is purposeful by identifying these categories upfront. If you must shift direction, begin by reassessing the planned initiative. Then, create new projects to help you achieve your objectives.
Prioritize your goals tactically
Your development pace may be ground to a stop if your team cannot agree on how to prioritize competing features. Allow strategy to assist you in deciding which elements on your roadmap should receive priority.
Goal prioritization is the “what” of the work. Plan out the details related to your efforts (linked to your goals). Then send it to your development team to be broken down into technical specifications.
The “how” of the job gets defined here. You’ll almost certainly end up with a queue of features linked to the plan and a team that understands how each piece of work adds to the overall objectives.
Your team may easily pick tasks from the top of the prioritized list, eliminating the need to speculate what follows next.
Collaboration between teams
Building exceptional goods in a short amount of time necessitates collaboration among several departments, spanning development, advertising, sales, support, and designing.
Since developers can offer realistic predictions on how long the work will require, development is one of the most critical teams product managers engage. Every team, though, is significant.
It would be best if you often communicated with everyone who influences the product and the consumer experience. The intention is to stay on pace and avoid repeating work.
