Distinctive Competence: The Art of Differentiating Your Product

Every company has a set of skills that it employs to make money. To the degree that specific competencies are unique to a given company, it may be able to fend off competitors, preserve or expand market share, and generate profits for years to come.
The fundamental mechanism through which all firms aim to maximize profits is developing and utilizing competencies.
Let’s start with a definition of competency.
Competency is everything a company excels at, and it can have multiple competencies.
For example, an advertising firm may excel at managing internal talent and developing leaders from within, or a manufacturing firm may be exceptionally successful in reducing the number of defects per thousand units produced.
Similar businesses can never succeed, and why should they?
That’s why business distinction is so crucial.
How do you stand out from crowds and create a one-of-a-kind company proposal?
It boils down to acquiring “distinctive competencies.” Try and learn more about how a distinct skill can give your organization a competitive advantage. First, look at our unique competence definition.
Companies work hard to improve their abilities and give a distinct value proposition to their clients. This comprises a set of advantages that customers won’t be able to get anywhere else but your company.
A company’s distinctive competency sets it apart from its competitors. It consists of a collection of valuable practices and technological talents that distinguish your company from the competition.
The unique skills increase your company’s reputation by raising brand awareness in your target market.
What Is Distinctive Competence?
Origin of Distinctive Competence
Between 1949 and 1957, Philip Selznick, a sociology professor at the University of California, Berkeley, investigated a variety of organizations.
Organizations like the Communist Party and the Tennessee Valley Authority were among them.
Philip noticed that each group has its strengths and limitations in his research.
The organization gained a sense of individuality as a result of these. He coined the phrase “distinctive competencies” in 1957 to describe this phenomenon.
Kenneth R. Andrews, an American professor credited with originating and popularising the notion of business strategy, enlarged on it a few years later, in 1971.
Andrews explained that the distinctive competencies were not simply the organization’s evident capabilities but also that it could execute better than its competitors.
A few years later, in 1976, Howard H. Stevenson, the Sarofim-Rock Baker Foundation Professor Emeritus at Harvard University, published a similar study.
Stevenson looked at six organizations and discovered that top executives had extremely varied perspectives of their company’s strengths and limitations and specific competencies.
Your company’s distinctive competence is what distinguishes it from its competitors.
Marketing, people, consumer relations, technology, manufacturing, and so on are all sectors where you can find specific skills.
Your competitors should refrain from replicating a skill or practice. If your company’s traits are easily replicable, they are unlikely to be considered a distinctive competency.
Customers can get more value from companies that have specific skills.
A distinguishing feature that is difficult to duplicate might give a company a competitive advantage. It motivates others to develop their firms, resulting in a more vibrant market.
To put it another way, let’s say this:
A trait, strength, or quality distinguishes a company from its competitors.
A distinctive competency could be anything: a distinguishing characteristic, a specific skill set, design, technology, unique branding, marketing, staff, or client base.
It doesn’t matter what it is as far as other businesses don’t use it.
Customers can receive more value from a company that has a specific skill. This distinguishes the company, product, or service from the competition and provides a significant competitive advantage.
Difference Between Core Competency and Distinctive Competency
Let’s look at core competency and how it differs from a distinctive competency.
In the sphere of management, the notion of core competencies was established.
In a 1990 Harvard Business Review article titled “The Core Competence of the Corporation,” C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel showed the notion.
They argued that a core competency is “a specific area of expertise that results from harmonizing complicated streams of technology and job activity.”
They used Honda’s engine expertise as an example, citing how it enabled the company to build well-regarded items such as lawnmowers, snowblowers, and vehicles.
Identifying and improving your company’s core capabilities might help you maintain a competitive advantage in the long run.
A core competency is a business competency critical to the company’s overall performance and success.
A manufacturing company with a low defect rate might not rely on it as a crucial business strategy, and an expected defect rate is a must-have skill if this is the case.
Per contra, if the same company marketed itself as a dependable manufacturer of high-quality goods, this could easily be a core strength.
The capacity to consistently deliver high-quality goods is critical to its business model.
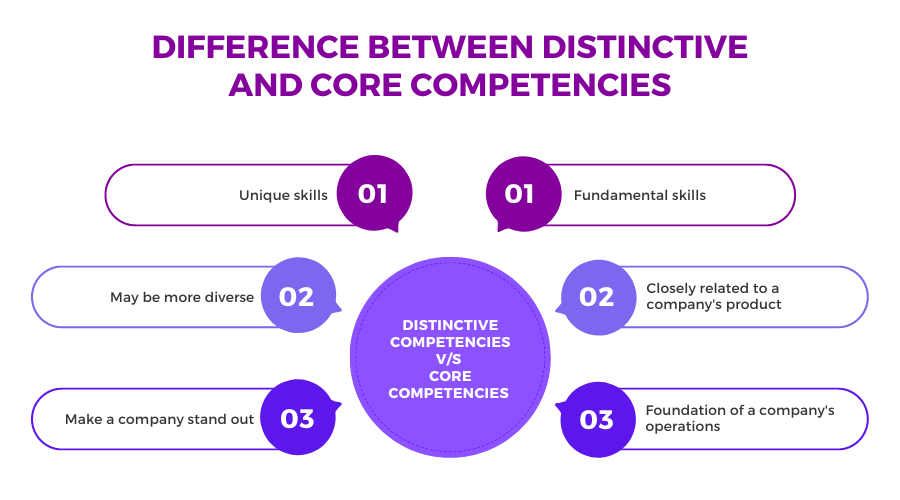
Core competencies set a business apart from its competitors and give it a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
A core competency, rather than physical or financial assets, refers to a company’s abilities or experience in a particular activity.
The strategic strength of an organization is its core competency. For example, Honda’s engine and propulsion systems, for example, are strategic strengths.
Sony, for example, has a specialization in miniaturization. Logistics and customer service are two of Federal Express’s strong suits.
You’ll undoubtedly come across the word “core competencies” while looking up the definition of distinctive competence.
Essentially, core competence is everything a company does exceptionally well. Therefore you can view it as critical to the company’s overall success.
For example, a marketing agency’s capacity to develop data-driven campaign concepts would be considered a core strength.
Apart from this, a distinctive competency is one-of-a-kind and provides a competitive edge.
When distinguishing between typical and core capabilities, a specific competence has a distinguishing trait that indicates it from a core competency.
Companies require core and distinctive competencies to succeed in the short and long term.
There is a distinction between core and distinctive competencies.
Core competency is the competency of business firms that has been crucial and central to their overall performance.
The company’s core skill allows it to address the critical success elements of specific consumer groups.
On the other hand, distinctive competency is the competitive value that enables the company to outperform its competitors (Bryson, Ackermann, Eden & Finn, 2004).
This ability serves as the foundation for gaining a competitive advantage.
Competitors need help to mimic distinctive competency.
It is observed that specific competency outperforms core competency.
Companies can also use this to put up a fierce fight against competitors in a competitive market setting, and it can set the company apart from the rest of its competitors.
As a result, to maintain a strong market position, businesses must focus on competencies.
Leigh Richards discusses the distinction:
“Any capability that distinguishes a corporation from its competitors is a distinctive competency.”
While any competency, core or otherwise, can be distinctive, it is often a core competency that distinguishes a company from its competitors.”
Why is Distinctive Competency Essential?
Developing a distinctive competency is critical to your company’s long-term success and provides you with a competitive advantage.
Still, it will also assist in boosting client loyalty because you will offer a unique service level to your company.
It’s also worth noting that the unique competencies of your company can shift over time.
As the market moves and new technologies or products emerge, your company’s skills may also need to go.
As a result, you should undertake internal business reviews regularly to guarantee that your unique competencies meet the demands of current market trends.
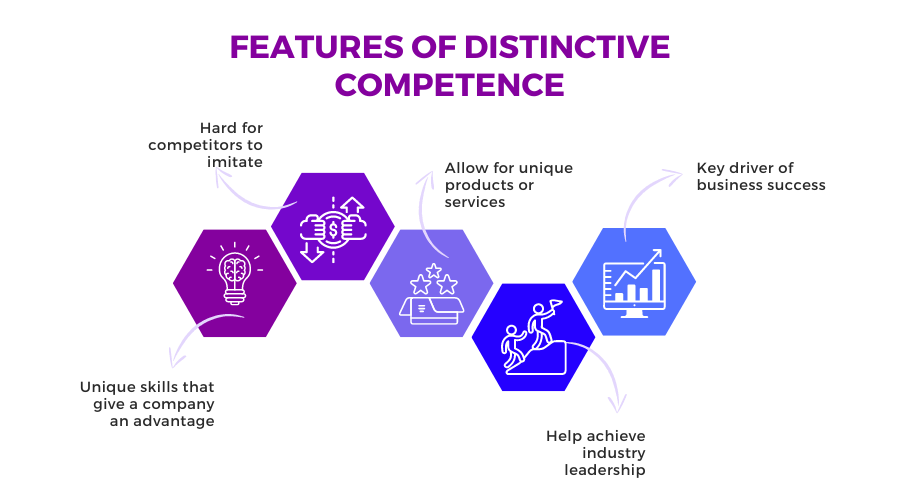
Companies with distinctive competencies can:
- Boost your competitive advantage
- Increase client satisfaction and loyalty.
- Set yourself distinct from the competition.
- Imitate with difficulty
- Boost the strategy
However, distinctive competence isn’t a given, and market changes and trends will unavoidably impact competencies.
As a result, those businesses rank higher that develop and reconfigure distinct competencies for long-term success in a constantly changing industry and environment.
One of the most significant benefits of diverse abilities is that they encourage fresh learning opportunities. This allows businesses to develop new tactics and concepts to stay ahead of the competition.
Developing the most successful separate talents frequently leads to great business strategies that benefit the entire firm, which also helps gain a competitive advantage.
Distinctive competencies provide a long-term competitive advantage that benefits the organization.
It enables the organization to focus on solving new problems as they arise rather than tackling the same ones repeatedly.
Distinctive Competence Examples
Let’s look at how this notion works in practice now that you know a little more about the definition of distinguishing competence.
Rigorous security measures, economies of scale, and lean manufacturing processes determine competency.
Let’s have a look at a few real-life examples of distinctive competence.
Amazon
Amazon has scoured the city for the most cutting-edge technical advances. Amazon can improve its products and services by being ahead of the curve in ideas and innovation.
It has been able to dramatically boost its output with the addition of talented and competent staff.
Amazon cultivates various abilities that generate outstanding customer experiences, such as speedy shipping and superior customer support, to be “the world’s most customer-centric corporation.”
Furthermore, the company’s distribution and workforce are distinct strengths.
To increase revenue, Amazon sells a wide range of products, giving customers a wide range of options.
Because of its brilliant marketing methods, it is well-known worldwide and has established a famous brand name, putting it ahead of its competition.
The e-commerce behemoth possesses a diverse set of distinguishing characteristics, including brand recognition, cutting-edge distribution, and a high- workforce.
Consider Google in comparison to any other search engine available. Google has been around for a considerable time and has a brand name that no other company can match.
As a result, Google’s brand name becomes a differentiating feature.
Above all, it has cemented its position as the most well-known search engine. Because other search engines find it difficult to reproduce this skill, Google has set itself apart from the competition.
Google has access to many resources that can help the brand get the attention it deserves.
The corporation can reach out to more people than any other organization since it has a competent marketing staff on board.
Its reputation as the most widely recognized search engine is a distinctive competency in addition to name recognition.
Google provides a wide range of high-end products and features that customers won’t find anywhere else.
Because of its sophisticated software infrastructure, Google has handily outperformed its competitors in every possible way.
Smaller businesses, such as an organic clothing line, can offer the specific expertise of sourcing high-quality, environmentally friendly materials from local suppliers.
Other companies, such as fast-food restaurants, food and beverage makers, and so on, benefit from brand recognition and being early product distributors, create a menu for products they sell, and then sharing on social media.
Conclusion
A successful organization has to learn the importance of consumer knowledge to adjust its business practices, such as production, distribution, price, and promotion, to meet consumer wants. You can achieve this by evaluating their resources and capabilities.
The consumer’s perception of the different competencies the organization and its competitors possess will help assess distinctive competence.
Specific competence results from an organization’s ability to deliver products and services that are perceived to be better than those offered by its competitors.
Distinctive competence is a perfect way to use a company’s strengths in a way that helps it not only stand out from its competitors but also surpass them.
There are many ways for a company to gain this kind of competence. They can do it by using something the target market needs or wants.
Still, the competitors need to offer, or the company could develop something existing companies don’t provide, making the customer choose their product.
