Top 7 Ways to Mitigate Product Development Risks
You can wonder about life without risks and uncertainties.
It would help if you took chances to develop.
And no one can reach their highest aspirations or live a happy life without occasionally taking risks.
Risk can be found in many different forms, such as taking the first step toward the goal of having a challenging conversation with a coworker.
Each time you…
- Pose inquiries
- Hire fresh talent
- Make fresh choices
You’re taking a chance.
Furthermore, in the field of product management, this is not an anomaly.
Making decisions and judgments amid ambiguity is one of the critical elements of product development.
In this writing, I’ll discuss the dangers and ambiguities that exist in the field of product development as well as several related topics.
What Is Product Development?
Generally speaking, product development refers to all phases of creating a product, from concept or idea to market release and beyond. In other words, the complete path of a product incorporates into product creation.
From the first stages of the product creation process to research and development, manufacturing, and distribution, numerous steps must be completed before a product is ready for market.
In the past, the build stage of the product lifecycle was equivalent to product development.
Product development involves much more than “how” a thing forms today. Involving cross-functional efforts from product management and engineering to product marketing, it is the “why,” “what,” and “when.”
Navin Iyengar once said, to build more robust designs, “Think of product development as a series of trials.”
Before launching your items on the market, it’s critical to guarantee that there is demand, that your final products are of the most excellent possible quality, and that your potential clients will receive value from them.
A new product can increase a company’s market share and spur expansion while generating new sources of income, ensuring economic sustainability.
Stages in Product Development:
Most of the millions of shoppers who make daily purchases need to be aware of the lengthy and challenging product development process every product must go through before being it to their shopping baskets.
Product development is a challenging yet exciting process.
The process of creating new goods and services can be uncertain. However, adhering to the systematic product development process can aid organizations in gaining clarity and confidence in the products they are creating.
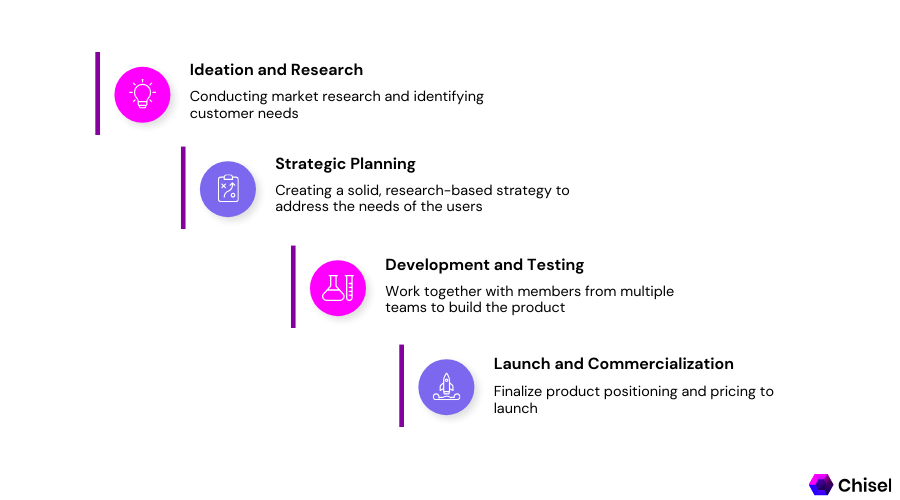
Generation of Ideas
Idea generation is the initial step in the product development process. At this stage, the business develops various original concepts based on internal and external resources.
This is the product innovation stage, where you develop product ideas based on market research, consumer demands, and concept testing.
The objective should be to provide many excellent ideas that can serve as the framework for the product development plan. This phase, more specifically defined in new product development, frequently follows a concept screening process to choose the next product endeavor.
Not coming up with concepts ready for implementation is the goal of this phase. Instead, discussions should focus on undeveloped, unproven ideas that can be nominated later.
Product Definition
It’s time to define the product after finishing the business case, discussing your target market, and examining its functioning. This goal, also known as scoping or concept development, is to improve the product strategy.
This phase in a startup is frequently known as discovery. In this stage, the design team comes together. The group determines the fundamental functionality of the new product concept and produces the first comprehensive assessment of its technical, market, and business elements.
Prototyping
Your team will thoroughly investigate and document the product throughout the prototyping stage by building it and writing a more in-depth business plan.
Best practices typically require thorough market analysis and a transparent project management strategy. The team develops a financial model for the new offering that makes assumptions about market share and thoroughly examines the competitive landscape for the new product and where the proposed product fits inside it.
These early prototypes could be as straightforward as a sketch or a trickier computer rendering of the original idea.
The preliminary design work would demonstrate technological viability at this point.
Initial design
Project stakeholders collaborate to create a mockup of the product based on the MVP prototype during the early design phase. The design should complement the primary functionalities of your product while keeping the target market in mind.
Creating the launch and manufacturing platforms to support the developing product is being done concurrently by marketing, sales, and manufacturing teams.
Testing and Validation
You must validate and test a new product before making it live. It guarantees that the product functions optimally before making it available to the general public, from development to marketing.
The finished product comes up for early client feedback at this point.
By concentrating on the following, significant understanding can be obtained:
- Choosing the focus group or the people who would profit from the newly developed product.
- Evaluation of additional options that might be offered to the focus group.
Commercialization
The next step is to commercialize your idea, which entails putting your website and product online.
You’ve now polished the design and tested the effectiveness of your development and marketing plan. Your final iteration should give you confidence, and you should prepare yourself to create your finished product.
The team, which includes project management, starts operationalizing the product’s manufacturing and customer support while assisting with its launch. This phase is known as the commercialization phase for this reason.
Product Development Risks and Uncertainties:
Wouldn’t it be incredible if creating a new product had all the benefits of innovation without drawbacks?
Unfortunately, manufacturing is always fraught with danger, and new items are no exception.
Technical Hazards
There’s a potential that your team will have blind spots or lack particular talents when integrating new technologies into a project, which could cause problems during development.
This is where NPI comes in: Adding capabilities to your project team and filling in knowledge gaps can be accomplished by bringing in outside expertise, such as an advanced manufacturing partner.
Risk of Significant Delays and Added Costs
Complex project control is challenging, and project managers often need more time or resources to finish the work.
On the other hand, creating software products is far more complex. They don’t grow linearly, and many of these activities are unique.
Cost Increases Come Up by Processing Work in Huge Batches
Processing work in large batches results in economies of scale and is more financially efficient and quicker.
On the other hand, large batches raise holding costs while lowering transaction costs and vice versa. Therefore, it is essential to balance the two charges to prevent the possibility of rising prices.
It is integral to keep things in perspective and use smaller batches because work-in-process is practically undetectable during the development of a product.
Market Dangers
The blooming of a new product can depend on several external factors, such as consumer perception, the state of the economy, and unforeseen events (the pandemic comes to our minds). When releasing a novel product to the market, time is frequently crucial.
If you release the technology too soon, buyers cannot fully grasp or appreciate it; if you remove it too late, your rivals will already be firmly entrenched as market leaders.
The Potential for a Poor Product Design
The dangers of poor product design are actual. Negative reviews, the departure of devoted clients, and severe harm to the bottom line can all follow from it.
Design thinking is fundamentally about comprehending and empathizing with your target audience. You can learn how to shape and build your project to address your client’s best’ wants, difficulties, and concerns by delving deeply into their needs, problems, and concerns.
Now, what about reducing these risks?
Let’s Look For Ways To Make Product Development Less Problematic:
Product development risk affects any business, regardless of size or experience level. Just so you’re aware.
- Elimination of risks is not possible if they are unknown. Try to establish assumptions as soon as possible.
Brainstorm all potential hazards and write them down. You organize all of your worries in this way.
Assign responsibility for each risk after creating a list of potential dangers and carefully considering them.
- It’s essential to have a well-defined, repeatable development process that enables time for assessing a product’s viability, whether you’re working with an outside business or assembling your team.
- Don’t be afraid, and don’t shy away from discussing dangers. Instead, pay close attention to how risks are discussed at team meetings and ensure that everyone in the team views risk management as a crucial component of the project.
- Your suggestion is fantastic. However, you must temporarily set aside your feelings and work objectively on your plan.
Making these tough decisions during this stage of your business will require you to act this way.
- Prioritization concentrates on the aspects of risk reduction that are most crucial. While working on the project, “what matters most” may change because some hazards have a more significant impact and probability than others.
- Ask three to five real consumers about their complaints and the solutions they’ve found in the past.
Take notes throughout these interviews, or even better, record them so you can review them later.
- Recently, assumption mapping has also received a lot of attention.
Things we assume to be true often have little to no supporting evidence. The product team should organize and validate these assumptions before developing and investing time and resources in building a minimum viable product.
While testing can be effective, you should concentrate your team’s experimental efforts in high-risk areas. You risk missing your window of opportunity and wasting your time if you don’t. Assumption mapping can be helpful in this situation.
Identification of dangerous assumptions about a novel good or service is known as assumption mapping. Understanding the presumptions about a new idea’s attractiveness, viability, and feasibility is hoped to produce better goods.
Asking, “What are all the things that need to be true for this idea to work” will help you comprehend the risk and uncertainty associated with your product.
It will enable you to recognize the attractiveness, feasibility, viability, and adaptability hypotheses underlie a company proposal.
Point to the following inquiries as part of your product development process:
Desirability: Is this notion in demand on the market?
Feasibility: Can we deliver on a large scale?
Viability: Is the concept financially viable?
Adaptability: Can the concept endure and change to fit a new situation?
Assumptions are frequently the basis for product decisions, so teams can better identify which areas require additional experimentation or development by outlining their assumptions.
If assumptions aren’t carefully thought out, they might be dangerous and even expensive if they turn out to be untrue or inaccurate.
This is why the assumptions mapping stage of product development is so important.
It is advised for all businesses, from small startups to established corporations, to reduce the danger of introducing a product unsuitable for the market.
Then, these hypotheses divide into four quadrants based on their importance and how well they are known.
Value proposition testing should assess the assumptions in the top right quadrant (unknown + significant).
Compare the known + critical items in the top left quadrant to your present roadmap and backlog.
More information can be obtained through the bottom right (unknown + unimportant) assumptions by conducting user interviews or using other testing techniques.
And deferring the bottom left quadrant (knowledge + irrelevant).
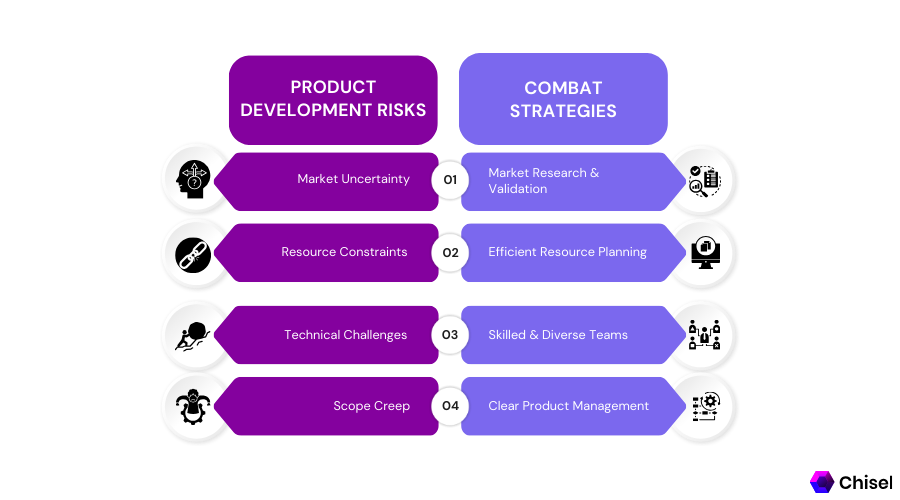
Conclusion:
Manufacturing new products in the market is a risk.
However, these dangers can be significantly reduced by putting the proper procedures in place.
And if you are new to the product management world, we urge you to look at the several tools on the internet. The best one on the market is Chisellabs right now!
Many of the risks connected with product development are mistakes we could avoid.
Every product development project after that is distinct in some way and necessitates a unique planning procedure with continuous adjustments.
You May Also Like:
- Product development methods: Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Waterfall
- Product Development Manager: Required skills and how are they different from Product Managers?
- How to Accelerate Product Development Process & Reduce TTM
- 7 Tips for Your Next Product Development Strategy
- Approaching the Perfect Product Development Strategy
