
What is the maturity model?
The Definition
Maturity models are simplified representations of an organization’s ability to continuously improve in a specific discipline. It assesses how successfully your firm evolves from a particular criterion, enabling you to examine a company’s maturity state.
A maturity model is technique organizations, and software development teams use to assess how well their business or project performs. And how capable they are of continual improvement.
Except for other goal-driven assessment methods, maturity models may analyze qualitative information. That is to establish a company’s long-term trajectory and performance.
Models get designed to determine whether firms are maturing. This means they continually test, expand, and improve.
Models define distinct levels of effectiveness. Also can pinpoint the current location of a person, team, project, or corporation within the model.
These are significant since they allow flexible performance monitoring that can disclose helpful health information.
It helps in understanding your product performance. Hence you can also decide if you are using product management tools and product roadmap software.
Whereas the models do not solve inefficiencies, they can focus on areas where businesses are not working at their best. And help them devise plans to enhance their operations and procedures.
How do you use the maturity model?
Companies utilize these to understand themselves. Models, for example, assist businesses in learning their maturity level. And how to improve within specific disciplines by asking questions and generating action plans.
It also assists firms in making better investment decisions.
For example, it can generalize progress estimations by determining how many resources are required. That is to advance from one level to the next.
Organizations use these to provide rough timing predictions. Such as assessing how long it takes the IT department to integrate new SaaS solutions.
Using completed work as a reference, the model helps frame generalizations.
Such as examining the number of level two to level three shifts done and observing that each change took two to three months.
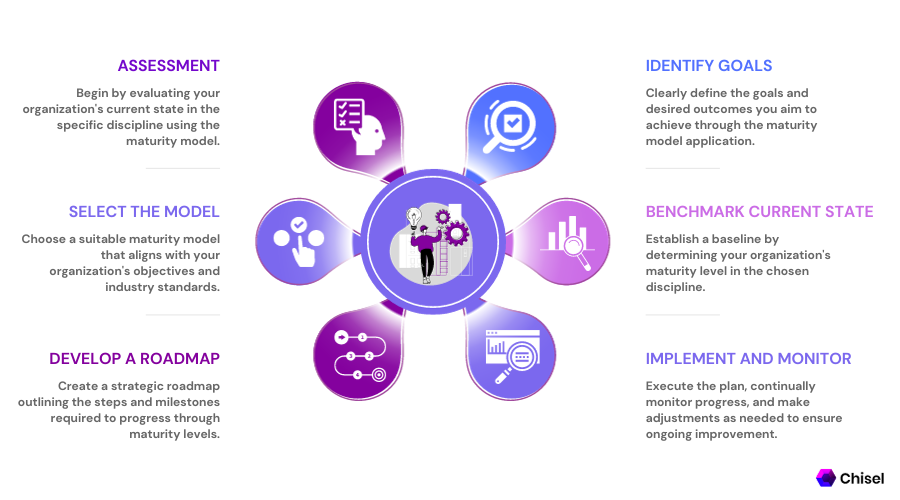
There is a three-step procedure.
Step 1: Evaluate Yourself
You must first assess your current degree of maturity. You can determine your stage simply by researching the maturity model of choice.
Some of these provide an assessment that you can use to eliminate some guesswork. Whatever method you use, you must first establish your present state.
Step 2: Decide How Far You Wish To Progress in Maturity
This may sound apparent, but once you realize where you are now, you can decide how far you want to go. In another sense, you would like to answer the question, “Do you want to grow your education staff or keep it small and shabby?”
Put another way. You don’t have to take your team to the end of maturity. You might prefer to take it up one notch.
That’s alright.
Your company’s culture also determines a majority of it. The idea is to identify that culture and establish your maturity level accordingly.
Step 3: Determine Any Gaps
Suppose you are at maturity phase one and wish to advance to stage four. There is a significant gap to bridge in such a case, and you will not have the means to do it overnight.
It would be best if you don’t attempt to skip to level four. “What steps do we need to do to get to stage two?” you must question yourself.
Next, establish goals and make preparations to get to phase two. Once you’ve reached level two, you can try to reach stage three again. You could also choose to stay at stage two, as we outlined in Step 2 above.
What are the types of maturity models?
There are various kinds of maturity models. The one you use may determine your industry or what you wish to analyze. Consider the following three model types:
Business Process Maturity Model
The business process model assesses an organization’s maturity using five stages. The levels are as follows:
- Initial: The lowest point is the starting level. It describes inconsistencies in management processes or teams who react to crises rather than anticipating them.
- Managed: The second level describes teams and businesses on a management basis. But individual sections within the company continue to work in silos with no communication or indication of implementing improvement ideas.
- Standardized: The standardized, or process management, level indicates that the company is aware of its processes. And strives for consistency and uniform delivery.
- Predictable: Organizations leverage their process infrastructure and asset capabilities to generate reliable results. By managing the variability in their outputs at the predictable level.
- Optimization: Businesses at this level are constantly improving and focusing on innovation.
Capability Maturity Model
Initially developed for software development, the capability maturity model evaluates a company’s or software development systems’ maturity. You do this by comparing it to best industry practices.
Businesses and development teams can use their models to evaluate their awareness of business processes.
This model is also beneficial for successful management approaches and opportunities for development by monitoring performance and allocating maturity levels.
All these, with some differences, characterize processes using the abovementioned levels. The levels in capability models are more clearly related to development processes.
Agile Iso Maturity Model
Unlike alternative models, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) model addresses some complaints against maturity models.
Agile models establish more properly specified expectations by standardizing the levels an international agency determines. Incorporating agile techniques might also assist enterprises.
Several of these are too simplistic to provide valuable evaluations.
Standardized agile approaches fight this by focusing on the different phases of the development life cycle.
Several agile techniques employ sprints to focus development teams and divide projects into more manageable segments.
An iterative development strategy enables teams to assess more subtle areas and discover areas for improvement more efficiently.
What are the benefits of using maturity models?
Prioritized Education
The emphasis on ongoing improvement and learning is one advantage of these. Many models don’t just display levels. They also explain how to go to the next level.
Suppose any of your processes are at a level one or two. In that case, there are frequent tactics you can implement to improve the levels of your operations and have your organization operating at peak efficiency.
Increased Capability
Another advantage of employing maturity models is their capacity to boost the competence of your firm or team.
Organizations can better identify opportunities for improvement by identifying present levels, shortcomings, and strengths.
Clearly defined levels allow for self-assessment and create tactics for encouraging growth and improved performance.
Suitable for a Wide Range of Audiences
Many of these began as software development tools. Still, they have been altered and integrated to function in various scenarios, business contexts, and sectors.
Teams of various sizes can use maturity models. Many contain defined metrics that make them more comparable and valuable to businesses.
Numerous variations within each of these can get tailored to your specific goals and circumstances.
There are ways these can help you grow as a firm and emphasize continuous improvement. It is regardless of your scale, business type, or present operational level.
Organizes Teams
The most significant benefit of maturity models is their capacity to link teams toward common goals and corporate objectives.
Because it assess qualitative development, they can assist businesses in developing internal strategic plans that tailor to their own needs and priorities.
They can also assist management and leadership teams to identify where their current approaches fall short.
Recognizing these flaws might assist them in incorporating gradual everyday modifications and raising the level of their operations. This frequently results in more efficient and successful workplaces and initiatives.
FAQs
A project management maturity model (abbreviated PMMM) is a matrix that depicts how a company’s project management plan grows over time. As an organization expands, so must its project management style.
A maturity model identifies areas where you may develop to obtain a higher level of maturity in your firm. It can benefit firms pursuing digital transformations because the models assist you in identifying problem areas to achieve your business objectives. Maturity models are also helpful since they stress learning and growth.
