What is Product Designer?

This article includes:
Product Designer Definition
A product designer controls a product’s customer experience with product management’s guidance entailing the company’s targets and strategies. Though product designers get most often linked with the visual and tactile components, they can also help with information architecture and system design.
What Is a Product Designer?
A product designer works to provide an optimal user experience while maintaining business objectives and product management goals.
They use different tools to resolve user experience issues and implement solutions to improve customer experience.
They play a vital role in the developmental stages of the product life cycle.
When you draft the initial design, product designers convey the product’s goals into the functional experience of the user. They provide feedback on critical functions you should implement while achieving these product goals.
Many companies hire a product designer even before hiring a product manager. Because they can contribute significantly to the kanban board, others delay having a product designer until later product life cycle stages.
Bonus: Click here to learn all about kanban.
Since you can outsource product design easily, companies hire contract-based product designers, consultants, or agencies for the role.
Product Designer vs. UX Designer
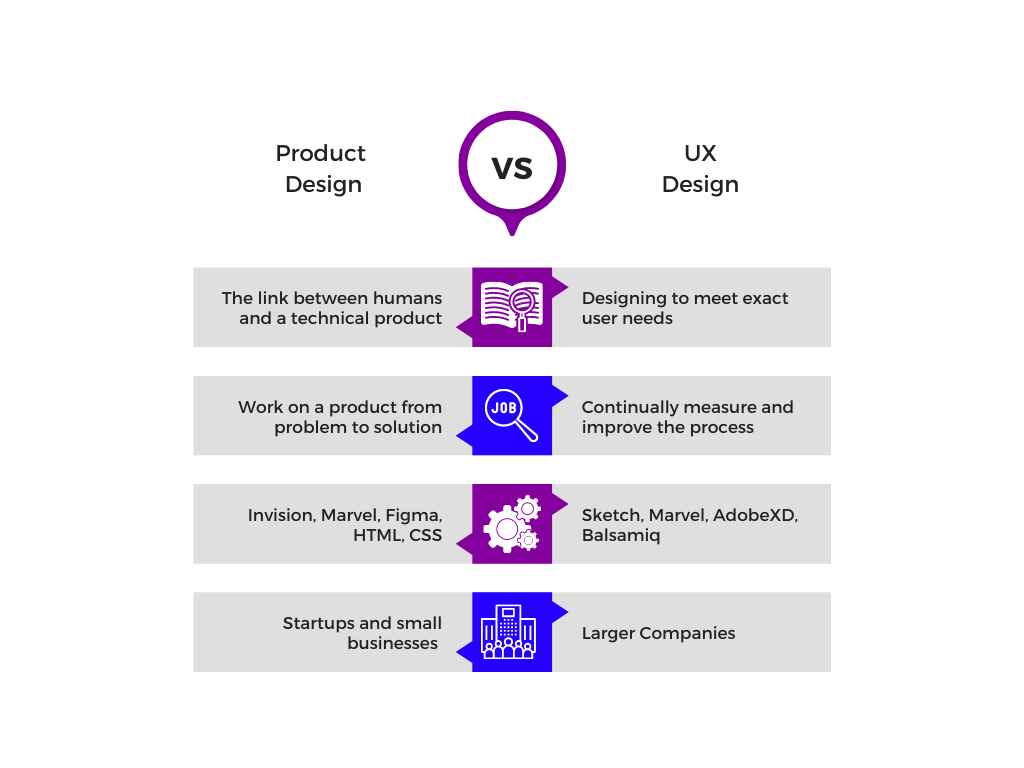
Before we start listing the differences, here’s the similarity.
We have already discussed what a product designer is. Both product and UX designers use a user-centered approach and design principles. They also use the same tools, such as wireframing and user mapping, and rely on market research.
Now here are the differences between the two. Product designers aim to make the designing process cost-effective, while UX designers aim to make it user-friendly. Product designers focus on the product’s value in the current economy, while UX designers focus on its ease to use.
Product designers emphasize branding, process, and the business regarding priorities. UX designers give more reputation to the usability of the product.
Product designers have a more comprehensive range of responsibilities compared to UX designers. Hence, product designers get paid higher than UX designers. The on-job demand for product designers is also higher than for UX designers. Even if you’re only on the start of your career, US job market offers a wide range of openings for junior product designers
Can a UX Designer Become a Product Designer?
Just because there are differences doesn’t mean a UX designer cannot become a product designer.
There are as many similarities between the two professions.
Both jobs are very similar, which is also interchangeable in many situations. Thus, UX designers can become product designers and vice versa.
What Does a Product Designer Do?
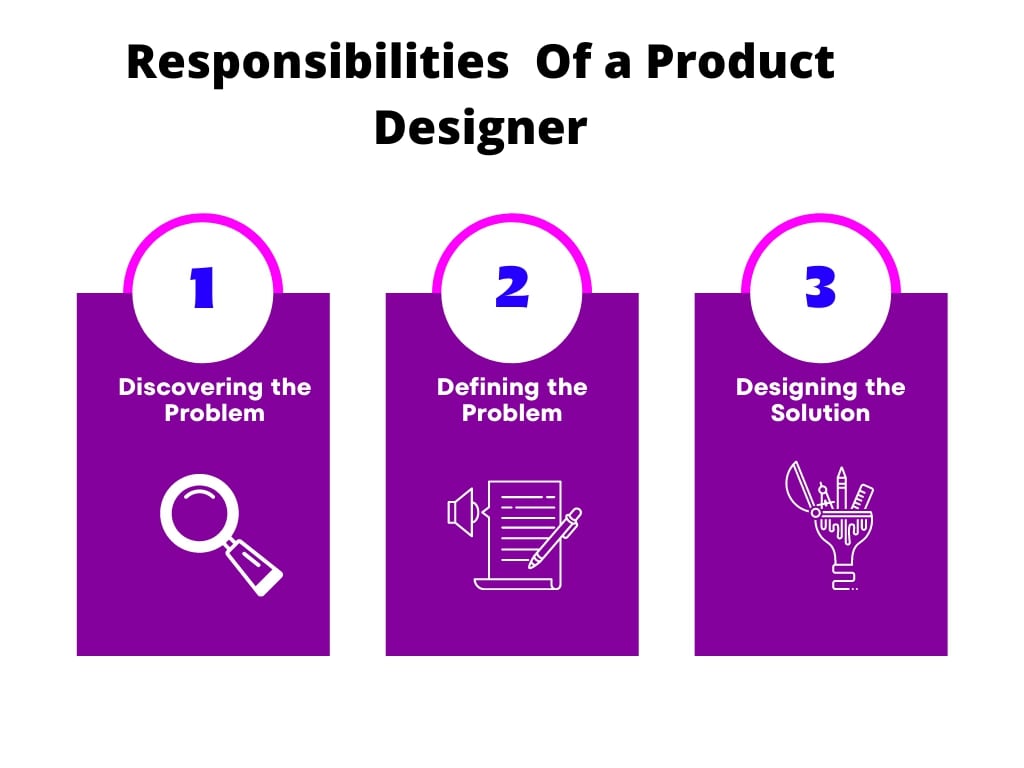
The role of a product designer differs from high-level functions such as system architecture to details like CSS templates.
Irrespective of their assigned work, the goal is to have a user-centric approach and improve the user experience.
Bonus: Want to learn how to conduct effective customer feedback management? Tap here right away!
There are several tasks that product designers deliver as a part of their job. Tasks include prototypes, wireframes, mockups, and user journey maps.
Product designers interact with clients to discuss the design concept, performance, and production criteria. Once in a while, they visit the client’s manufacturing unit to examine the practicality of production.
A traditional role of product designers was to give them the product with a set of requirements.
These tasks included sketching the design, analyzing the feasibility, and raw material availability. However, product designers work alongside the development team throughout the developmental stage.
Since their involvement is from the beginning, product designers can influence the ‘what’s’ and ‘hows’ of the product’s development. They use design thinking principles and keep the user at the forefront.
Along with the team, they develop design concepts using CAD while keeping the budget in mind. They also organize team meetings that could be specific or multidisciplinary by nature.
The core responsibility of product designers lies within the four stages of designing. Steps include designing, modeling, prototyping, and conducting user testing.
The stages could also involve coding with front-end languages. As in HTML or CSS to create logos, animations, buttons, icons, digital products, assets, and text.
Additional responsibilities come in when the product is physical or hardware. These responsibilities include selecting colors, textures, and materials, recommending manufacturing methods, and using 3D prints for prototypes. Product designers maintain a digital guide of the product suite for future reference.
For outsourced products, product designers also need to carry out administrative duties.
Skills Needed to Become a Product Designer:
Though the job requirements of a product designer may differ from organization to organization, the following are the skills that are usually required.
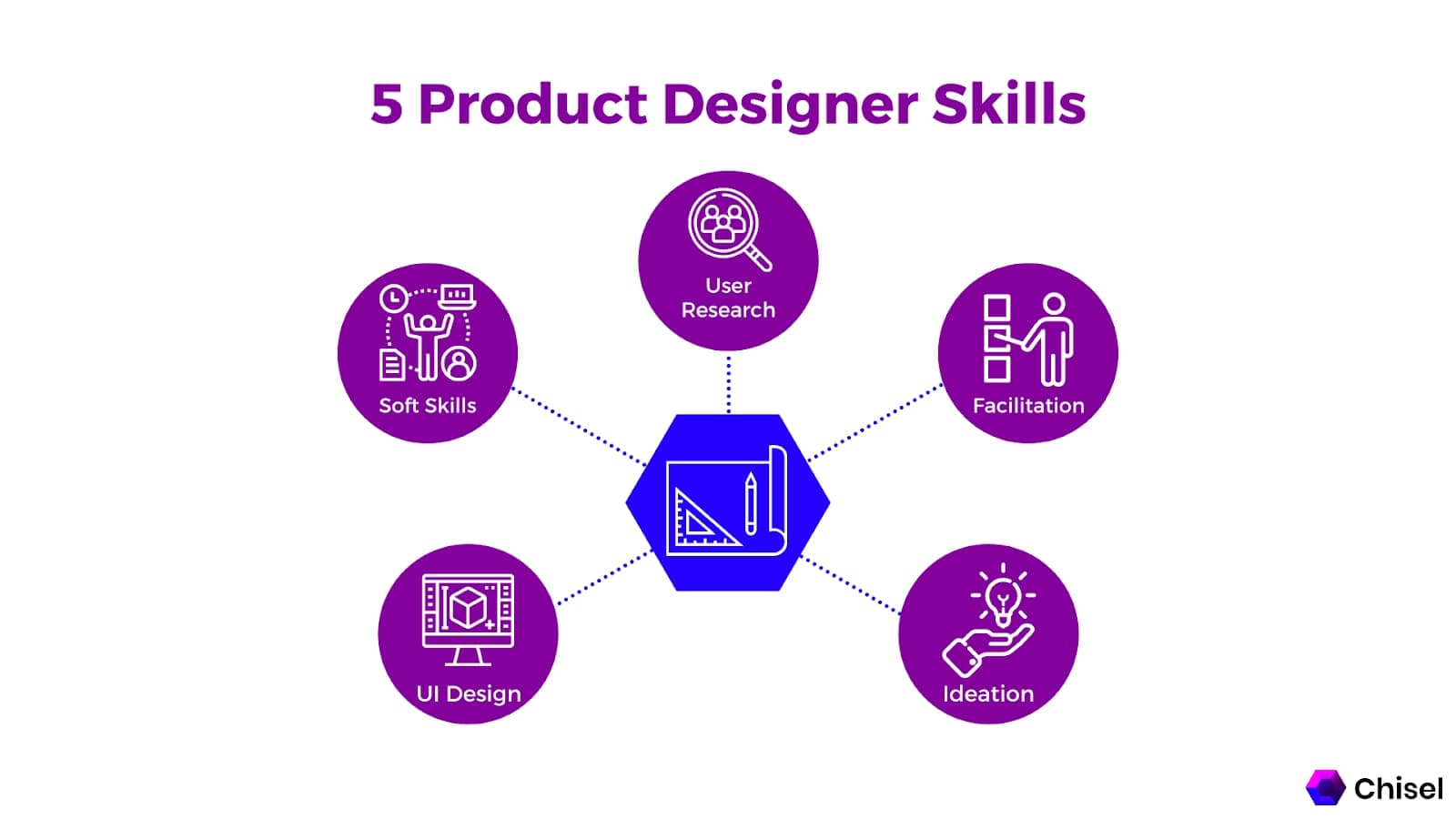
User Research
Decisions that product designers make depend on qualitative and quantitative data.
As a result, they require skills that concern acquiring this data in the first place. These skills include interviewing, observation, and questioning.
The ultimate goal of user research is to understand the end-user, which is why mastering analytics is crucial.
You can gather the user’s knowledge through interviews, questionnaires, and observation. It transfers into three forms: personae, jobs-to-be-done, and experience maps.
Try Chisel’s too good to be true features that make the entire product management seamless.
Facilitation
Facilitation is the set of implementations done during and after a meeting with the team. The objective is to ideate the product and design it.
Along with communication skills, this responsibility requires UX design skills to organize UX workshops.
Product designers pick out needed stakeholders for various workshops – tech-based, marketing, business, legal, and more. Throughout the workshop, they should guide the participants through either animation or storytelling.
Ideation
User research helps develop product ideas, features for the prototype, or upgrades. Ideas are acquired using the user’s insights or design workshops.
Product designers are concerned with providing the best user experience. To test the knowledge, product designers need to master UX assessment skills.
Such tasks may require them to use product management software like Chisel.
Product designers have information architecture skills that help set up the company’s mobile application and website. Tracing all user-flows or wire flows, which requires workflow skills, is crucial to understanding the user’s interaction with the product.
UI Design
UI facilitates all the interaction between the product and the user. The product designer must be an expert behind it. Anything from conveying brand identity to making it aesthetically pleasing and coherent.
The product designer needs to know visual design principles such as balance, hierarchy, typography, and proximity to create harmony in the product.
They use interaction design principles for understanding different interactions between the product and the user. For instance: scroll animation.
Soft Skills
Product designers require many soft skills.
One such skill is empathy: understanding the user’s problems and perspective.
Collaboration is another essential skill because product designers often work with other team members. The product designer must be a team player to work with product managers and collaborate on product roadmap software.
Along with collaboration, effective communication is essential. It’s hard to organize workshops and present ideas without effective communication.
Product designing is a highly fast-evolving field. Thus, your design must keep up with the latest trends.
A product designer needs to be curious and seek out knowledge proactively to keep their work up to date.
Knowledge of agile frameworks such as scrum and kanban comes in handy when working with organizations with an agile framework.
How To Become a Product Designer?
Understand how to use your tools:
Your UI and UX drawing applications are an extended version of you. Mastering your tools implies recognizing where the buttons are and how to utilize them. Insert, drag, rotate, export, trim and erase images.
YouTube lessons or sitting next to a designer colleague and observing them work are great ways to understand the fundamentals. It’s effective if you get more comfortable and proficient with a good drawing application.
Having a decent workflow is also a vital aspect of understanding your tools. The way you organize your files is also your workflow. Workflow addresses everything from naming files to arranging folders, exporting resources, and organizing levels within a file.
Other designers, managers, and clients cannot follow your organizing thought process if you do not have a defined workflow.
Subfolders and poorly titled PNGs make it easy to get misplaced. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to workflow setup, and various designers at different firms use different methods.
Explain your approach:
Designers who can’t explain their thought processes lack the design framework to support their decisions with evidence and analysis. You must control yourself and your process at the most remarkable organizations. If you don’t have a procedure in place at a company, they will instruct you what to do most of the time.
It’s critical to explain how you came up with your design and why it addressed an issue for specific individuals because it equates to monetary terms for a company.
Create a portfolio of work:
Work on the project type for which you want to get employed. People find it challenging to use their imagination.
Thus, if your portfolio consists only of emoticon bundles, you won’t be good at developing medical device software. Make sure your portfolio contains the types of projects relevant to the job you’re seeking.
Utilize your portfolio to strengthen your visual design skills. If you don’t believe a product looks good enough artistically but knows it answers the issue, now is your chance to impress.
Enroll in relevant courses to improve your understanding of core design concepts such as hierarchy, proportion, color theory, and scale.
Request feedback from a designer colleague on your creation. It’s time to tweak the aesthetics and give it that polished look that appears impressive on modern design sites. That is after you can explain the methodology of your work and the ways it handles an issue.
What Are the Goals a Product Designer Should Set?
Outline the design process in detail:
Suppose you’re a sound designer and a good listener. In that case, you can usually figure out what people are attempting to achieve from what they aren’t saying and appearing on your screen. Such attentiveness makes people appreciate you. For early-stage companies and design crises, it’s an essential skill.
Make sure you know what you’re going to deliver and when you’re going to do it:
These are some questions that people will have but will rarely ask:
- When it comes to these designs, how likely are they to evolve?
- What about fonts, symbols, and pictures? How definitive are they?
- Will you depict the interaction, or will it remain static?
- Are you displaying only the most basic use cases or a variety of extreme circumstances and scenarios?
- Will everything get done, or will it just be ‘sufficient to get started?
Recover and make amends:
If an emergency arises and you can’t provide what you committed, contact the concerned personnel immediately and provide a strategy to get back in gear.
Check if this is the most practical/effective approach for the people working on your project.
What are some fantastic tools a product designer uses?
InVision:
Prototyping, teamwork, and exact workflow are all made easier with inVision. It allows you to cost-effectively build interactive mockups for your creative projects and wireframes.
Why is it so popular among product designers?
Its collaborative capabilities embed into the product’s fabric. Product designers may take a specific collection of interface concepts. Then connect the ideas to create a functional prototype, get immediate feedback, and manage the entire design process within one integrated product ecosystem. Many designers’ workflows revolve around InVision’s product design tool.
Pricing: They provide one working prototype for free. Every month, paid plans begin at £10.44/US$15.
Blobmaker:
Blobmaker is a practical graphic design tool for quickly creating informal, unique, and organic SVG forms. We recommend such design tools for high-end projects.
Why is it so popular among digital product designers?
Product designers appreciate thematic design components to create branding, detach content on a page, add backgrounds, and compare interface elements.
Pricing: It’s a dynamic design tool that’s completely free.
IconJar:
IconJar is an icon management program that allows you to save, browse, preview, use, and transfer icons in one location.
Why is it so popular among digital product designers?
You may use the tool to manage and alter icons in any style, including SVGs and PNGs, and you can even rapidly add icon fonts. Rather than using fragile clue cards, it will create SVGs and extract all characters as distinct symbols.
Pricing: This design tool is free to trial for 14 days. On SETAPP, charges are $9.99 per month.
Sip:
Sip is a sophisticated color picker tool for product designers that makes it easier to collect, organize, and edit a wide range of colors. It allows you to share different colors with everyone and integrate them into other workflow tools.
Why is it so popular among digital product designers?
Colors, like fonts, play an essential role in any product designer’s process. Sip shines when it comes to being organized and inspired by your color schemes.
The software uses practically every conceivable color format. It comes with many valuable add-ons that operate with your entire operating system and browser of choice.
Pricing: The entire cost per device is INR 879.99.
Figma:
This Figma tool includes exclusive innovations like Vector Networks and Arc tools and design features you already know.
Figma takes things a step further by allowing you to bring your design ideas to life. It can be utilized on the cloud platform and does not involve the installation or exporting.
Why is it so popular among digital product designers?
Figma is a tool for working on design projects that is both quick and efficient. Its files are up to date, and sharing designs across the firm is straightforward with this platform, making cooperation a breeze.
Pricing: Every user’s Figma subscription costs $12.00 per month.
Adobe XD:
Thanks to Adobe XD, you can communicate your narrative with authentic designs that feel authentic. It’s an ultimate UI/UX design tool that allows you to create wireframes and animation, experiment, and work on your designs.
Why is it so popular among digital product designers?
With the help of Adobe XD, you can view a design and immediately understand how the final product feels. Product designers may use Adobe XD to be more inventive and communicate with their teams more effectively.
Pricing: A user’s Adobe XD subscription costs $9.99 per month.
Conclusion
Product designers have some of the most critical roles in the business. Hiring a good one can make or break a successful business.
